Ptosis Repair with Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
In some situations, patients have both ptosis and dermatochalasis; as such a single surgical procedure is adequate. Surgery to correct ptosis repair is directed to elevate the eyelid height (open the eye wider). In contrast, surgery to correct the dermatochalasis is called a blepharoplasty - and its goal is to remove the excess skin (and herniated orbital fat) that is present on the upper eyelids; this skin might or might not be interfering with peripheral vision.
Each surgical condition requires a distinct surgical approach. Let's originally elaborate on each of the two conditions:
(1) What is Ptosis?
Ptosis, may also be called blepharoptosis refers to droopy eyelids due to an abnormally low upper eyelid in the relaxed primary position. This might result in loss of vision particularly while reading, headaches and eyebrow strain.
- Ptosis is classified in several ways based on a variety of characteristics.
- Based on origin, it might be congenital or acquired.
- Based on etiology, it is classified as aponeurotic, myogenic, neurogenic, or mechanical.
- Based on levator function, it is divided into ptosis with poor levator function (0-5 mm), moderate levator function (5-10 mm), or good levator function (≥ 11 mm)

Upper eyelid ptosis is drooping of the upper eyelid margin in relation to the superior limbus and causes functional and cosmetic problems. A ptotic eyelid covers more than 2 mm of the upper limbus, and in severe cases it covers the pupils obstructing vision.
Who gets an Upper Eyelid Ptosis?
It is particularly seen in elderly patients who have undergone cataract extraction or lens replacement and is supposedly due to stretching or disruption of the levator muscle by retractors during lens surgery.
Causes of Upper Eyelid Ptosis
Upper eyelid ptosis might be true ptosis or pseudoptosis.
True ptosis can be congenital or acquired.
Ptosis might also arise due to complex facial injuries resulting in levator detachment from the superior tarsal plate.
Symptoms and Signs of Upper Eyelid Ptosis
- High tarsal fold
- Persistent wrinkles in the forehead due to contraction of the frontalis muscle
- Asymmetric elevation of the eyebrows with greater effect on the affected side
- Substantial cases present with restricted visual fields
Various techniques have been used for correcting upper eyelid ptosis. Some of the techniques include:
- Suspension of the lid from the frontalis muscle: Done for patients with poor levator function (
- Resecting segment of the levator muscle: Done in patients with poor levator function but having severe ptosis (≥ 4 mm).
- Plication of distal levator muscle aponeurosis: Done in patients with good levator function (>10 mm) to achieve long-term correction of ptosis.
- Fasanella-Servat mullerectomy: For patients with minor ptosis (10 mm excursion).
- Transpalpebral blepharoplasty plication of the levator aponeurosis: In patients undergoing cosmetic facial surgery.
- Müller muscle–conjunctival resection repair: In patients with mild-to-moderate ptosis alone under general anaesthesia.
- Levator advancement under local anaesthesia: In patient with moderate-to-severe ptosis using patient cooperation during the surgical procedure.
(2) Dermatochalasis - may also be called Pseudoptosis is presence of excess skin
- Substantial blepharochalasia
- Excess skin and / or herniated orbital fat
- Changes in ocular volume
Surgical correction of dermatochalasis or pseudoptosis is performed via a blepharoplasty surgery.

What is Blepharoplasty?
- Your eyes including your eyelids, are perhaps one of the originally things people notice in you. This makes your eyes and eyelids one of the most important components for an appealing facial expression and aesthetic appearance. Any visible change in the shape or size of the orbital or periorbital region can spoil the look of your face.
- As you age and grow older, your eyelids might become ‘droopy’ or ‘baggy’ due to the stretching of your eyelid skin and gradually decreasing tone of your eyelid muscles. Your droopy eyelids and brow together cut a sorry figure for your face making you look tired, sleepy and haggard, further leading to eyelid or brow straining or both. In extreme cases, your saggy, baggy eyelids can even obstruct your vision, particularly peripheral vision causing difficulty in reading or driving.
- Blepharoplasty ensures cosmetic or functional corrections to the area around your eyes to beautify your look or to correct any abnormalities in function.
Defining Blepharoplasty
- The term blepharoplasty is derived from the Greek ‘blepharon’ which means ‘eyelid’ and ‘plassein’ which means ‘to form’. Simply put, blepharoplasty is a plastic surgical procedure that is used for correcting defects, deformities, and disfigurations of the eyelids, and more recently, it has been used for achieving aesthetic modification of the periorbital region of the face.
- Blepharoplasty may be erroneously referred to as an ‘eyelift’ or “eyelid lift” as the procedure does not involve lifting of the eye or eyelids in any manner. It might be done to achieve either functional or cosmetic ends or a combination of both.
- Blepharoplasty involves removal or repositioning of excess tissue as well as reinforcement of surrounding muscles and tendons to reshape the upper eyelid, lower eyelid or both.
Indications of Combined Upper Lid Ptosis with Upper Blepharoplasty
Presence of both conditions (1) Ptosis and (2) excess skin. Of note insurance generally will not pay for both procedures to be performed at the same time. Often, the upper blepharoplasty is performed at the same time as the ptosis surgery, but paid for by the patient. Altneratively, some patients elect to proceed in a staged-fashion: originally undergoing ptosis repair to elevate the eyelid and thereafter, in a separate surgery -months later- undergoing an upper blepharoplasty.
Also, often when the ptosis is corrected, the amount of skin on the upper eyelid becomes more prominent or noticeable. Thus might patients, opt to undergo cosmetic upper blepharoplasty to remove and sculpt the upper eyelid excess skin and fat.
As the ptotic eyelid is elevated, restored to its normal position, the skin that is present on the upper eyelid bunches up and wrinkles more-slide the slider control to the write and note how when all the way to the right - the eyelid is more open, but NOW the skin is lapping over the edge of the eyelid.
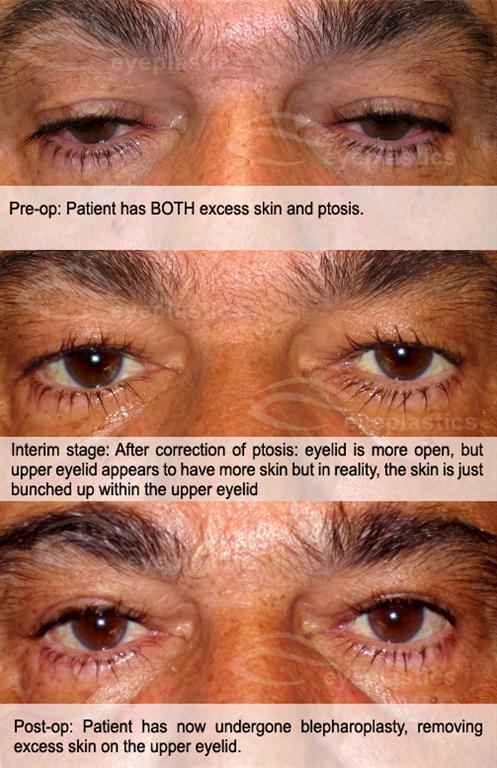
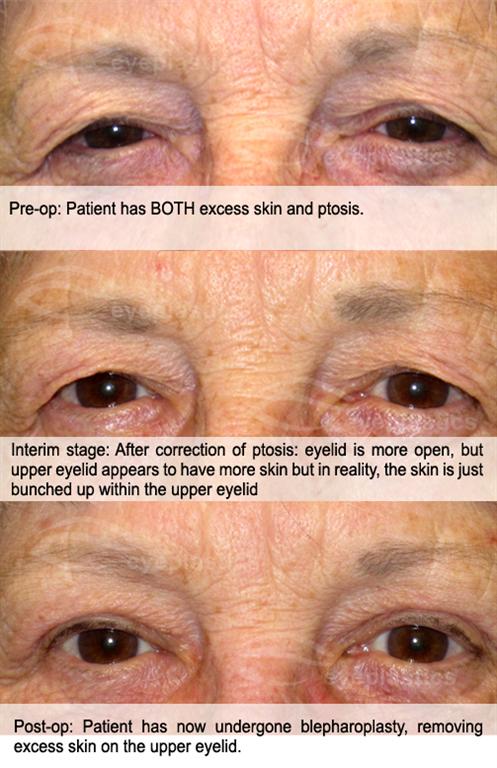
The following figures show the before and after scenarios of upper blepharoplasty with ptosis.
As the eyelid ptosis is corrected (the muscle is adjusted to elevate the eyelid), the edge of the eyelid and the upper eyelid skin move closer together.
The animation below illustrates the scenario when there the patient has ptosis BUT ALSO has with some amount of excess upper eyelid skin
If there is excess upper eyelid skin, once the ptosis is corrected, the skin my OVERHANG the edge of the eyelid: Slide the control to the right to see a demonstration of this effect.
As the eyelid is elevated, the skin that is present on the upper eyelid, bunches up (accordion effect). The upper eyelid skin might roll over the edge of the eyelid); slide control to the far right to see this effect.
View the sample photographs below to see patients who have undergone COMBINED ptosis with upper Blepharoplasty.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




