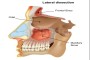
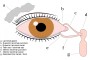
Congenital Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction
Overview, Signs and Symptoms of an Obstruction
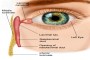
- The lacrimal gland produces tears which enter into the "duct"
that drain the tears from the eye into the nose. The most common symptoms are If one has a plugged up "tear duct," not only will tears spill over the eyelids and
run down the face, but the stagnant tears within the system can become infected.
- excess tearing (tears could run down the face) and
- mucous discharge
- This could lead to recurrent red eyes and infections.
- The excessive tearing can also produce secondary skin changes on the lower eyelids.
-
Congenital congenital
Congenital Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction
Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction (NLDO) is very common in infants.
- Children are commonly born with an obstruction within the "tear duct." In fact, 6% of all children are born before their tear ducts are open.
- The stagnant tears within the "tear duct" often become infected causing pus (heavy matter) to collect between the eyelids.
- Antibiotics could help some of the symptoms, BUT this is not cure for the blockage
- Such obstructions could resolve spontaneously within the initially few months of life. In fact, 95% of these children will show resolution before their initially birthday. If it does not resolve surgery could be necessary.
Blockage presents in one of four ways:
- simple obstruction
- congenital fistula (as seen in the photo)
- acute dacryocystitis
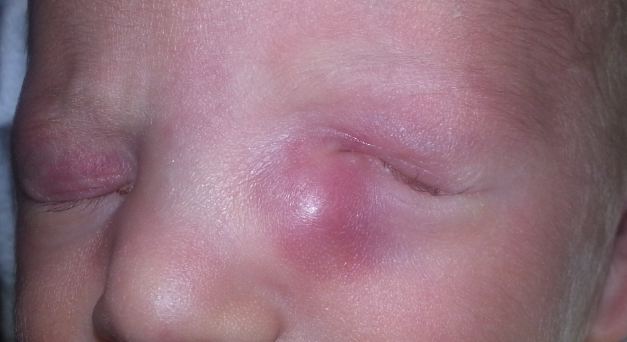
- congenital dacryocele or mucocele

Dacryocystocele or Dacryocele
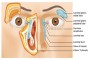
Location of Blockage & Anatomy
The very end of this duct is the most common place for blockage to occur. This site is called the valve of Hasner at the distal nasolacrimal duct and could represent failure of canalization of the epithelial cells that form the duct.
Medical Treatment of Congenital Obstructions
- Many of these do open on their own given time.
- Massaging from the tear sac in the could help create a pressure wave that can open the blockage.
Surgical Treatments



![A photograph of [describe what the image depicts here], with embedded text that says [describe the embedded text here].](/public/images/gallery/thumb_images/1343787448-1343787448-image-1.jpg)